Plugin Architecture
The plugin operates under a dual-execution model:
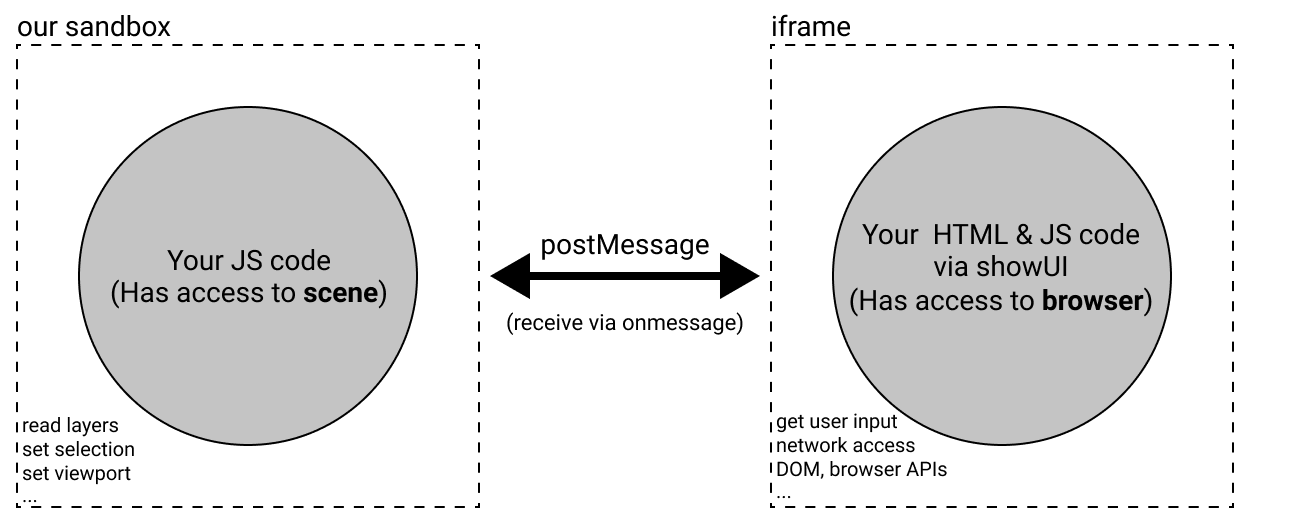
Sandbox Environment:
- Executes the main code in an isolated JavaScript environment.
- Has direct access to the Figma API for operations such as reading layers and modifying nodes.
UI Environment (iframe):
- Manages the user interface and interactions.
- Has full access to browser APIs.
Communication:
- Uses
postMessagefor communication between the sandbox and the user interface.
Anatomy of a Figma Plugin
Plugin development is primarily done using web technologies like HTML, JavaScript, and CSS. Both plugins and widgets run in a sandbox to ensure a secure environment.
Figma uses an execution model where the plugin's code runs on the main thread within a sandbox. The sandbox is a minimal JavaScript environment and does not expose browser APIs.
This means you have access to all standard ES6+ JavaScript, including standard types, JSON and Promise APIs, binary types like Uint8Array, etc. However, there is also a minimal version of the console API, and Web APIs like XMLHttpRequest, Workers, and the DOM are not directly available from the sandbox.
Communication between the browser and Figma.com
- The Figma application is loaded from the
figma.comdomain over the internet. - The browser acts as the environment where both Figma's main code and the plugins developed for the platform are executed.
Browser Environment and Plugin Execution
- When a plugin runs in Figma, an isolated execution environment is created using WebAssembly and QuickJS. This sandbox environment ensures that the plugin operates securely, preventing unauthorized access to external resources.
- The plugin's code can interact with the Figma API to:
- Read data from the file, such as layers or nodes.
- Modify properties, make selections, and set views within the file.
Using iframes for the User Interface
- If the plugin needs to display a user interface, Figma runs the visual part of the plugin inside an
iframe. Thisiframeis decoupled from the sandbox environment and allows:- Displaying the plugin's HTML and JavaScript content.
- Accessing browser APIs like DOM manipulation and capturing user events.
- The
iframeis subject to a Content Security Policy (CSP) to prevent unauthorized access to external resources.
Communication between the Sandbox and iframe Environments
- Communication between the sandbox environment (where the plugin's code runs) and the
iframe(which contains the graphical interface) is done using thepostMessageAPI. - In the sandbox environment:
The plugin's code has access to the Figma "scene." This allows for operations like reading layers, modifying nodes, adjusting selections, and setting the file's view. Additionally, these "scene" properties cannot be sent to the
iframeviapostMessage. - In the iframe:
- The HTML and JavaScript code has full access to browser APIs.
- It is responsible for handling user interaction, such as clicks, forms, or any other UI-related events.
- Messages sent via
postMessageensure a clear separation between Figma's editing functions and the interface's interactions.