Introduction
The Back-End adopts the "AWS First" principle, prioritizing the use of native AWS services and infrastructure. Custom solutions will only be developed when standard AWS services do not efficiently meet a specific requirement.
Architecture
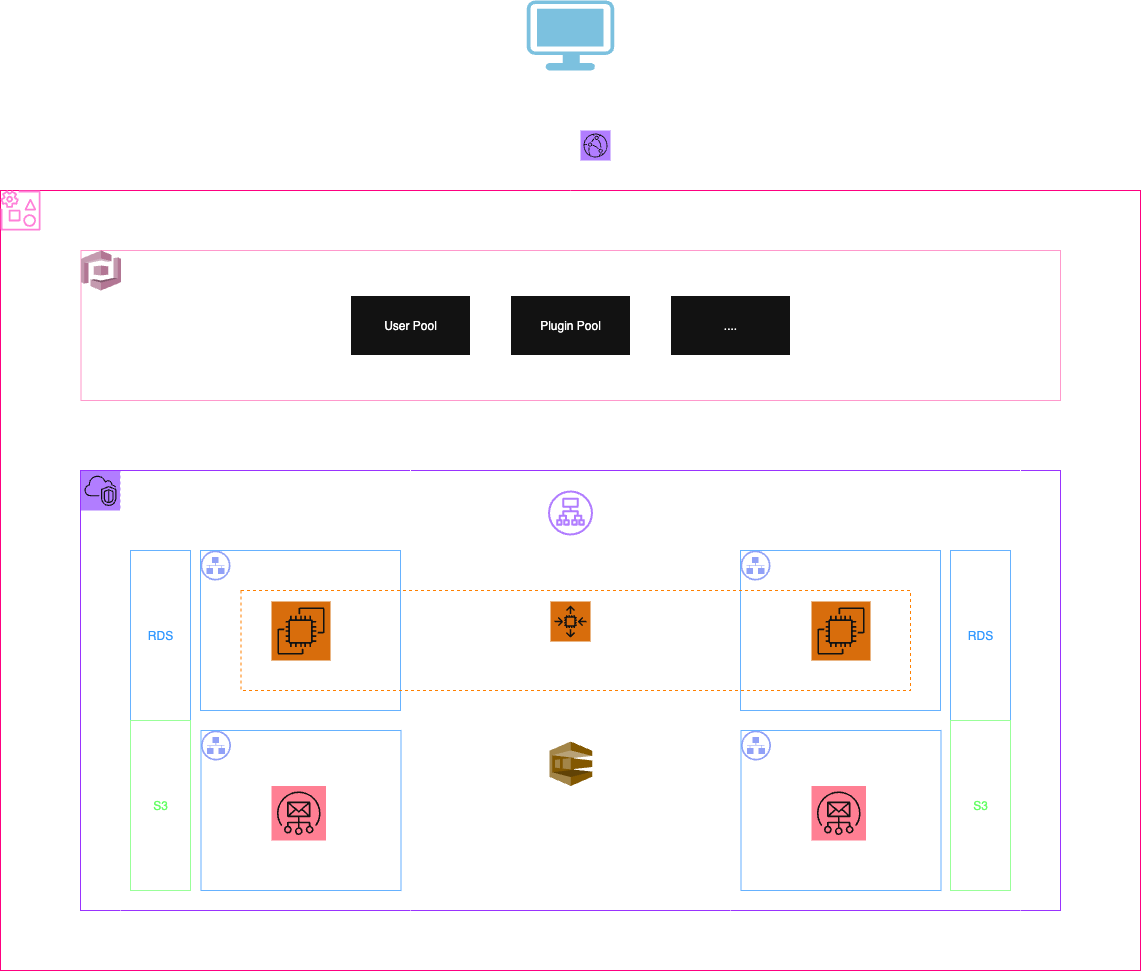
The proposed architecture is multi-tenant, allowing resources to be segmented per customer. This separation ensures that one customer's load or usage does not affect the performance or availability of others, ensuring scalability, security, and isolation.
Explanation
The infrastructure isolates each customer, providing an identical but separate architecture across different Availability Zones. Thus, high traffic from one customer does not impact other tenants, ensuring a robust and efficient environment.
Pillars
- Cognito: Manages authentication and allows integration with SAML providers such as Okta for efficient session handling and restricted access to services.
- VPC (Virtual Private Cloud): Allows creating a private, isolated virtual network within AWS where subnets, access rules, and security policies can be defined. The VPC provides full control over the network environment, facilitating resource segmentation, protection against unauthorized access, and secure integration with other services or on-premises networks. This is fundamental to ensure the security and isolation of each customer's resources.
- Application Load Balancer (ALB): The entry point for web traffic (HTTP/HTTPS). The ALB distributes requests among available servers, can handle TLS certificates (for HTTPS), and route traffic by domain or path. It is deployed across multiple Availability Zones to ensure high availability and automatic load balancing.
- Subnet: A subdivision of the network within the VPC. There are public subnets (with Internet access via NAT or Internet Gateway) and private subnets (where applications and databases reside without direct Internet access). Pairs of subnets are created in each Availability Zone to ensure redundancy and high availability.
- EC2: Virtual servers where the main services that contain the business logic run. Other services, such as Lambdas, can connect to these servers to access key functionality.
- Auto Scaling Group: Enables automatic adjustment of the number of EC2 instances based on demand. It monitors metrics like CPU usage or network traffic and, according to defined policies, increases or decreases the number of available servers. This ensures high availability, cost optimization, and responsiveness to workload variations.
- RDS: A managed relational database service in AWS that simplifies creating, operating, and scaling databases, automatically handling tasks like backups, updates, and failover.
- S3: Amazon S3 is an AWS service that allows storing and retrieving any amount of files securely, scalably, and with high availability from the cloud.